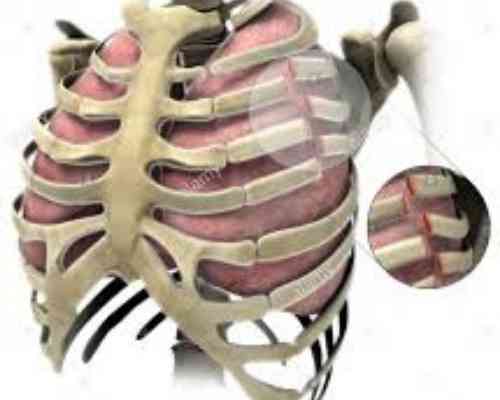
What is Costochondral Separation? | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment
What is Costochondral Joint?
It is an articulation between the costal cartilage and the ribs at the ventral aspect of the ribcage. Costochondral joint exists between first the ribs. Floating ribs don’t articulate with the costal cartilage, and though with the rib cage.
What is Costochondral Separation?
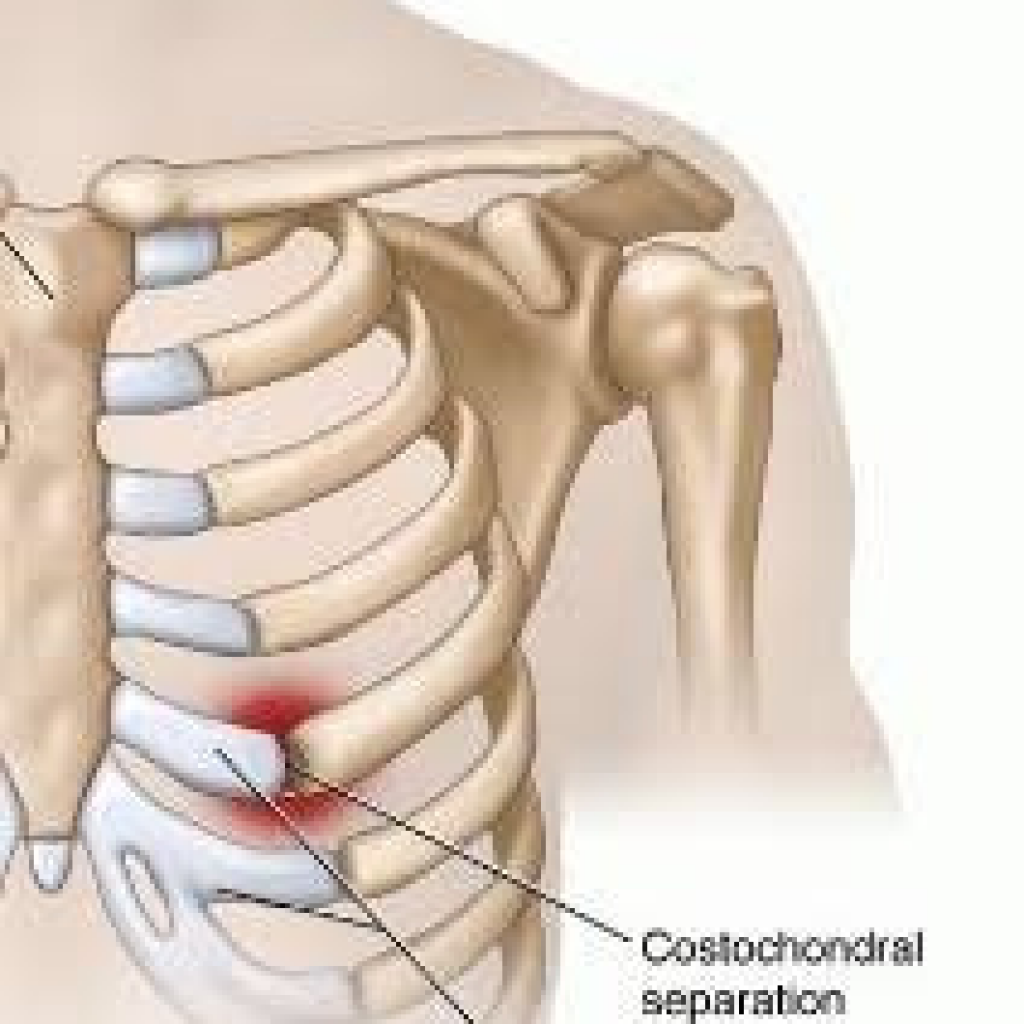
Costochondral separation is an injury that is characterized by the subluxation or dislocation of the Costochondral joint. It is also known as “Separated Rib Syndrome” or “Slipping Rib Syndrome”.
Also, the costal cartilage tip gets disconnected from the attached rib and protrude over the lower rib, cartilage, or neurovascular bundles in the mediastinum.
How is deep breathing beneficial for your skin?
Costochondral Osteochondral Separation and It’s Consequences
Costochondral separation affects the first ten ribs, as the Costochondral joint only exists between the first ten ribs and their costal cartilages.
The frequent causes of Costochondral separation are:
- A sudden blow or impact force to the thorax.
- Blunt force to the thorax
- Motor vehicle accident (MVA)
- Fall from a considerable height
- Hypermobility of Costochondral joints.
- Sports trauma
- Sudden, violent twisting movement of the trunk
- Severe constant cough
- Costochondritis may also lead to Costochondral separation
- Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis are also the leading causes of Costochondral separation.
- Further, Costochondral separation is more prevalent among females and adults over the age of 40.
Clinical Anatomy of Relevant Joints
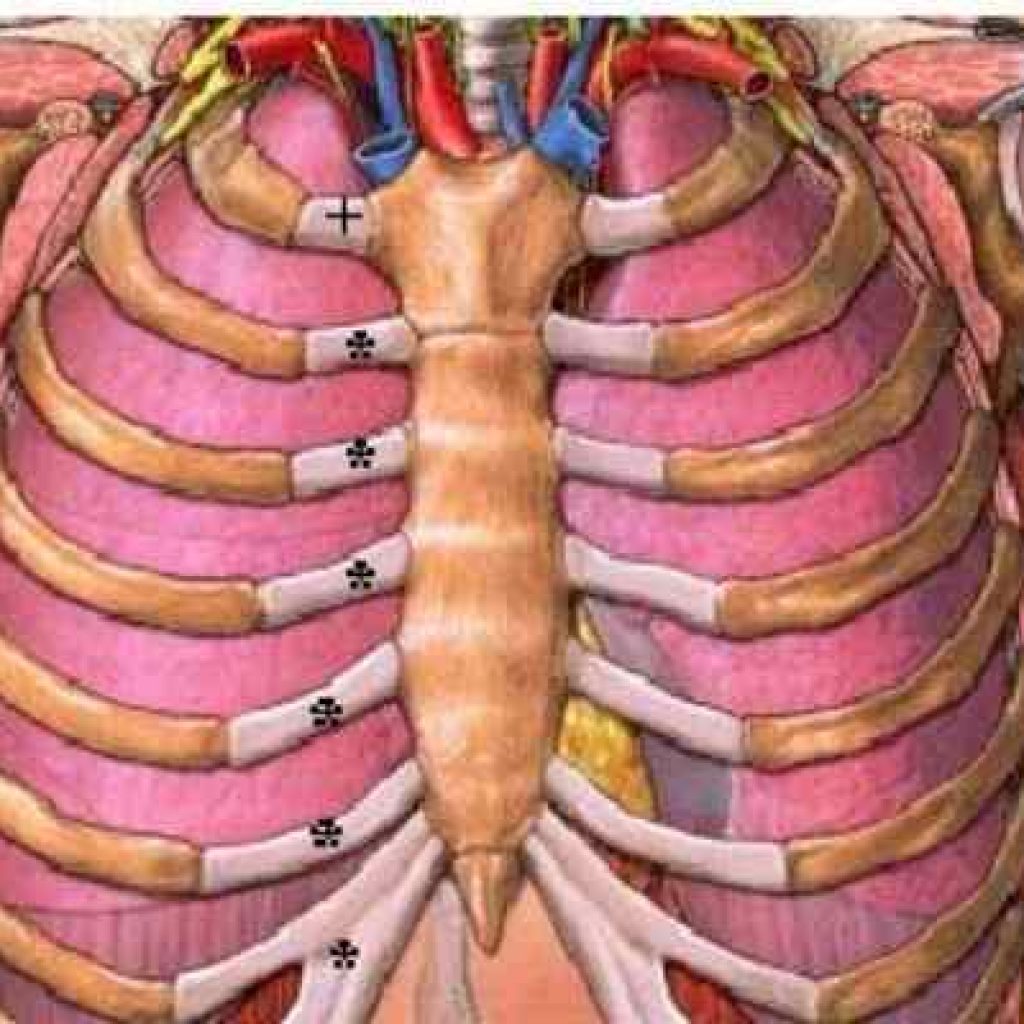
The costochondral joint is a landmark between ossified and unossified parts of the thoracic wall that connect the costal cartilages and the sternal end of the ribs with the sternum. Furthermore, there are twelve pairs of ribs and ten pairs of Costochondral joints.
The costal cartilage is hyaline cartilage except for ninth and tenth costal cartilage, which are fibrous. Therefore, The Costochondral joints are structurally classified as primary cartilaginous joints or synchondrosis. Intercostal neurovascular tissues supply these joints.
What is FEMINISM?
Bio-Mechanics of Relevant Joints
The movement occurs as a whole in the thorax. Additionally, individual Costochondral joints are fixed articulations that possess zero degrees of movement and are functionally termed synarthrosis.
Difference between Costochondritis and Costochondral Separation
Firstly, the two terms are different from each other. Costochondritis is an inflammatory process that affects the costal cartilage in response to an infection of the chest wall. Also, Costochondritis may lead to a Costochondral separation. Moreover, Costochondral separation is a cleavage between the rib and its costal cartilage.
Clinical Presentation
Signs
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Muscle spasm
- Deformity of the rib cage, and
- Crepitus on examination
Symptoms
- Sharp, throbbing pain in the chest.
- The pain will aggravate with exertion, coughing, sneezing, hiccuping, and defecation.
- The pain will become worst with inspiration and expiration and reported as breathing difficulty.
- Also, pain may increase with the change of posture.
- Tingling and burning sensation at the site of injury.
- The patient will also complain about the radiating symptoms if there is pinching of the intercostal nerve.
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Procedures
- EXAMINATION will demonstrate bruising, swelling, deformity, and grunting sound on palpation.
- MRI is the preferred tool to diagnose Costochondral separation.
- ULTRASOUND AND CT-SCAN are used to distinguish between Costochondral separation and a rib fracture.
- An X-ray will help your healthcare professional to find out if there is multiple ribs fracture.
Management
Conservative
Costochondral separation often heals up on its own within 2-3 months. Your healthcare practitioner will recommend you to take painkillers, NSAIDs, multivitamins, and do plenty of rest to restore the injury until the symptoms get subside.
Non- Conservative
If the injury is severe and multiple ribs are involved; your healthcare practitioner may suggest a surgical procedure to repair the loss. Moreover, your healthcare practitioner will do a Surgical Thoracotomy if you have a Filial chest, and Severe damage to the heart lungs, or pleura.
Physiotherapy
Cryotherapy
Initially, apply a cold pack over the injured site for 15-20 minutes. It will help reduce inflammation, reduce pain, generate a soothing effect, and promote the healing process.
Exercise
No doubt Costochondral separation can be a quite severe condition if you are not following precautions. But Don’t be sedentary and do some gentle exercises that draw little exertion but are great in efficacy and assist your healing process. The disease process may, indeed reduce your strength and endurance.
However, if you do gentle exercises daily, your pre-existing muscular strength and endurance will at least remain the same.
Additionally, to-do-list of exercises is as follows. All the activities are performed twice a day with 10-15 repetitions of each. There is also a person-to-person variation that exists. You should consult a physiotherapist at least once so that he or she will design your home physiotherapy program.
- Kinesiotaping
- Breathing Exercises
- Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBTs)
- Interdigital Technique (IDTs)
- Pursed Lip Breathing
- Blowing exercise
- Incentive Spirometry
- Diaphragmatic Breathing
- General Exercises
- Ankle Pumps
- Calf Stretch
- Straight Leg Raise (SLR)
- Cross-Legged Ankle Pumps
- Isometric and Isotonic Quads
- Pelvic Rolling and Bridging
- Walk for 30 minutes
- Recumbent bike for 15-20 min
- Gentle stretchings of upper limbs
- Rhythmic and gentle trunk movements in all directions.
- The affected individual can also use assistive devices (such as an assistive Bed Ladder in later stages) to improve their bed mobility.
What are the Symptoms of Sour Stomach?
Clinical measures
Indications
In case of any acute injury, do not forget to apply the PRICE formula of first aid. That is:
Protection of injured area from further injury
- Take as much rest as possible.
- Icing to prevent excessive swelling and profuse bleeding. Therefore, do not apply ice directly. Use a gel-filled cold/ice pack.
- Gentle compression to support the area and stop the bleeding.
- Elevation of the affected area to reduce swelling. (This rule is generally applicable for the extremities to elevate the part above the heart level)
- Support the injured area by gently pressing both the hands over the chest or holding a soft pillow against your chest during coughing and sneezing.
Contraindications
Avoid wrapping a bandage around the chest because it will restrict your movement and breathing.
- Avoid unnecessary movement of the trunk.
- Stay hydrated to compensate for the fluid loss.
- Suppose your healthcare practitioner has restricted your trunk movement in one or more directions. Must remember, do not do those movements. Thus, take all the precautions and follow the guidelines today. Indeed, You will be healthy and fit tomorrow.
Conclusion
Costochondral separation can be a life-threatening condition and should not be underestimated even if you got a slight blow to the chest.
Visit a healthcare practitioner or an emergency care service immediately after the thorax trauma to prevent further loss. Severe trauma to the chest wall may also result in some lethal injuries in the Ruptured aorta, Lung collapse, Heart failure, damage to the Pericardium, Pleura, Mediastinum, Liver, and Spleen. Be cautious and be careful about your health, fitness, and life. Hence, these are precious and worthwhile.
Also, if you have ever seen or come across such type of fatal injury. Share your experience by scrolling down to the comment section.
What Are the Most Common Causes of Blackheads?
Read More Articles






[…] What is Costochondral Separation? | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment […]
[…] What is Costochondral Separation? | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment […]
[…] What is Costochondral Separation? | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment […]
[…] What is Costochondral Separation? | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment […]